Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Static Field Simulation#
Example of static field generation.
This examples show how to generate a static field (i.e., B0) map starting from the object susceptibility distribution.
The static field is written as the following convolution (performed as a pointwise multiplication in the Fourier space):
where \(\chi(\mathbf{k})\) is the Fourier transform of susceptibility spatial distribution and \(D(\mathbf{k})\) is the dipole kernel defined by:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from mrtwin import shepplogan_phantom, b0field
Generate susceptibility distribution#
First, we generate a 3D Shepp-Logan phantom:
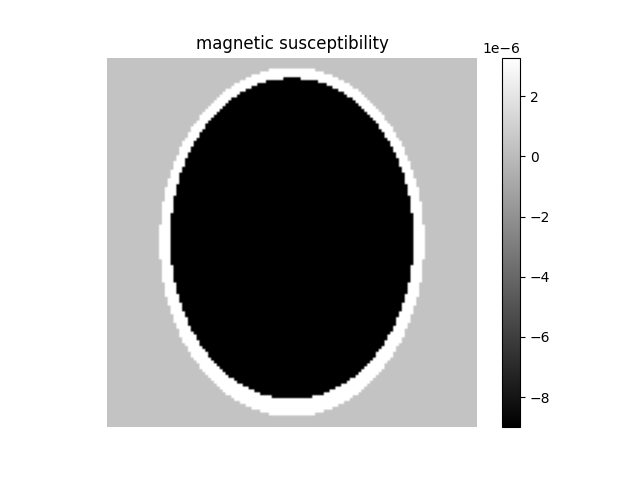
phantom = shepplogan_phantom(ndim=3, shape=128, segtype=False)
# Get susceptibility
chi = phantom.Chi
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(chi[64], cmap="gray"), plt.axis("off"), plt.colorbar(), plt.title(
"magnetic susceptibility"
)
plt.show()
Basic Usage#
Starting from the susceptibility distribution, we can generate the corresponding static field perturbation as:
b0map = b0field(chi)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(b0map[64], cmap="turbo", vmin=-300, vmax=300), plt.axis(
"off"
), plt.colorbar(), plt.title("B0 map [Hz]")
plt.show()
![B0 map [Hz]](../../../_images/sphx_glr_example_staticfield_002.png)
Optionally, we can provide a mask of the object to exclude the background:
mask = phantom.M0 != 0.0
b0map = b0field(chi, mask=mask)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(b0map[64], cmap="turbo", vmin=-300, vmax=300), plt.axis(
"off"
), plt.colorbar(), plt.title("masked B0 map [Hz]")
plt.show()
![masked B0 map [Hz]](../../../_images/sphx_glr_example_staticfield_003.png)
The static field map calculated by default for a field strength of 1.5 T.
This can be changed via the B0 argument:
# B0 strengths
B0 = [0.55, 1.5, 3.0, 7.0, 11.7, 13.3] # field strengths in [T]
# Generate phantoms with different field strengths
b0maps = [b0field(chi, B0=strength) for strength in B0]
# Display
b0map = np.concatenate([b0map[64] for b0map in b0maps], axis=1)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(b0map, cmap="turbo", vmin=-300, vmax=300), plt.axis(
"off"
), plt.colorbar(), plt.title("B0 map [Hz]")
plt.show()
![B0 map [Hz]](../../../_images/sphx_glr_example_staticfield_004.png)
As an alternative, we can force a specific
B0 offset range using the b0range argument as:
b0map = b0field(chi, b0range=(-500, 500))
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(b0map[64], cmap="turbo", vmin=-300, vmax=300), plt.axis(
"off"
), plt.colorbar(), plt.title("B0 map [Hz]")
plt.show()
![B0 map [Hz]](../../../_images/sphx_glr_example_staticfield_005.png)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.520 seconds)